PX4 is an excellent open source autopilot stack. They have offer Software-in-the-loop(SITL) and hardware-in-the-loop(HITL) simulation out-of-the-box. In addition to that, you can integrate with their simulator using MAVROS in the same you would be talking to a real vehicle. Let’s see the steps to setup PX4 SITL + Gazebo locally.
Installation
There are a few scripts to create a development environment on https://dev.px4.io/en/setup/dev_env_linux_ubuntu.html for Ubuntu, and other links for other platforms. After taking a look at the scripts, I decided to try the installation step by step to understand the process better.
First, I cloned the PX4 code:
git clone git@github.com:PX4/Firmware.git
On the installation page, I started following the instructions beginning on Permission Setup
Persmissions and general dependencies
sudo usermod -a - G dialout $USER
This group is described here:
dialout: Full and direct access to serial ports. Members of this group can reconfigure the modem, dial anywhere, etc.
I was not planning of connecting to anything because I want to run the simulator, but I did it anyway.
Then remove the modemmanager as recommended.
sudo apt-get remove modemmanager
There are a few packages we need to install, but I just a few were missing on my system:
sudo apt-get install genromfs exiftool
Python related dependencies
Required python packages
sudo apt-get install python-argparse python-empy
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
Note, selecting 'libpython2.7-stdlib' instead of 'python-argparse'
python-empy is already the newest version (3.3.2-1build1).
python-empy set to manually installed.
libpython2.7-stdlib is already the newest version (2.7.12-1ubuntu0~16.04.4).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Both were installed already.
My pip version is 8.1.1, so I needed an update there.
sudo -H pip install --upgrade pip
And then install some packages:
sudo -H pip install pandas jinja2 pyserial cerberus
Also pyylog even it was optional:
sudo -H pip install pyulog
FastRTPS installation
The installation went smothly with the instructions here:
wget http://www.eprosima.com/index.php/component/ars/repository/eprosima-fast-rtps/eprosima-fast-rtps-1-5-0/eprosima_fastrtps-1-5-0-linux-tar-gz -O eprosima_fastrtps-1-5-0-linux.tar.gz
tar -xzf eprosima_fastrtps-1-5-0-linux.tar.gz eProsima_FastRTPS-1.5.0-Linux/
tar -xzf eprosima_fastrtps-1-5-0-linux.tar.gz requiredcomponents
tar -xzf requiredcomponents/eProsima_FastCDR-1.0.7-Linux.tar.gz
It doesn’t need to be in the home directory; it could be anywhere you have space. Make part in the next instruction could take some time, but it is ok. I did the make and configure part one by one, but it can be done as suggested in a single line:
cd eProsima_FastCDR-1.0.7-Linux; ./configure --libdir=/usr/lib; make -j2; sudo make install
cd ..
cd eProsima_FastRTPS-1.5.0-Linux; ./configure --libdir=/usr/lib; make -j2; sudo make install
cd ..
rm -rf requiredcomponents eprosima_fastrtps-1-5-0-linux.tar.gz
ROS/Gazebo dependencies
I have installed a full ROS Kinetic Kane installation; so, I got a few steps done already. Some shared libraries needed for this part were installed already as well(protobuf-compiler, libeigen3-dev and libopencv-dev). I also had installed mavros and mavros-extras; so, I skipped the installation from the source recommended on the instructions
apt-cache pkgnames | grep ros-kinetic-mavros
ros-kinetic-mavros
ros-kinetic-mavros-extras
ros-kinetic-mavros-msgs
Making and running
Installation requirements are done. To run the simulator, we need to pick a model and run a make command that makes the code and run the simulator at the same time. Pick the first target on the documentation and try it:
cd Firmware
make posix_sitl_default gazebo
...
[ 0%] Building CXX object src/lib/DriverFramework/framework/src/CMakeFiles/df_driver_framework.dir/DriverFramework.cpp.o
('python import error: ', ImportError('No module named toml',))
Required python packages not installed.
On a GNU/Linux or MacOS system please run:
sudo pip install numpy toml
...
src/lib/mixer/CMakeFiles/mixer_gen.dir/build.make:82: recipe for target 'src/lib/mixer/mixer_multirotor.generated.h' failed
make[4]: *** [src/lib/mixer/mixer_multirotor.generated.h] Error 1
CMakeFiles/Makefile2:4154: recipe for target 'src/lib/mixer/CMakeFiles/mixer_gen.dir/all' failed
make[3]: *** [src/lib/mixer/CMakeFiles/mixer_gen.dir/all] Error 2
make[3]: *** Waiting for unfinished jobs....
('python import error: ', ImportError('No module named toml',))
Required python packages not installed.
On a GNU/Linux or MacOS system please run:
sudo pip install numpy toml
Got two errors even when:
sudo apt-cache pkgnames | grep python-toml
python-toml
The package was there. Let’s follow the instruction again:
sudo -H pip install numpy toml
make posix_sitl_default gazebo
This time it works! Gazebo started showing a standing drone waiting for commands:
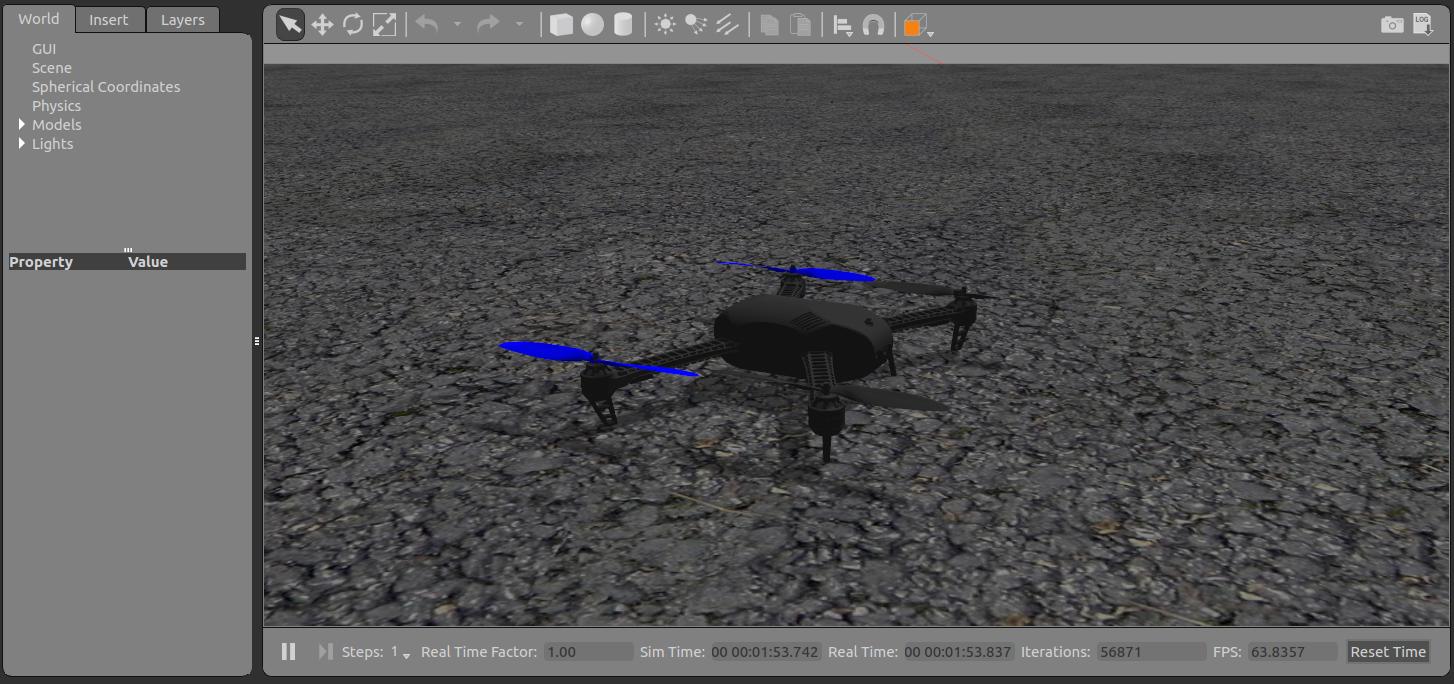
Let’s see how the other vehicles look like:
-
3DR Solo (
make posix gazebo_solo)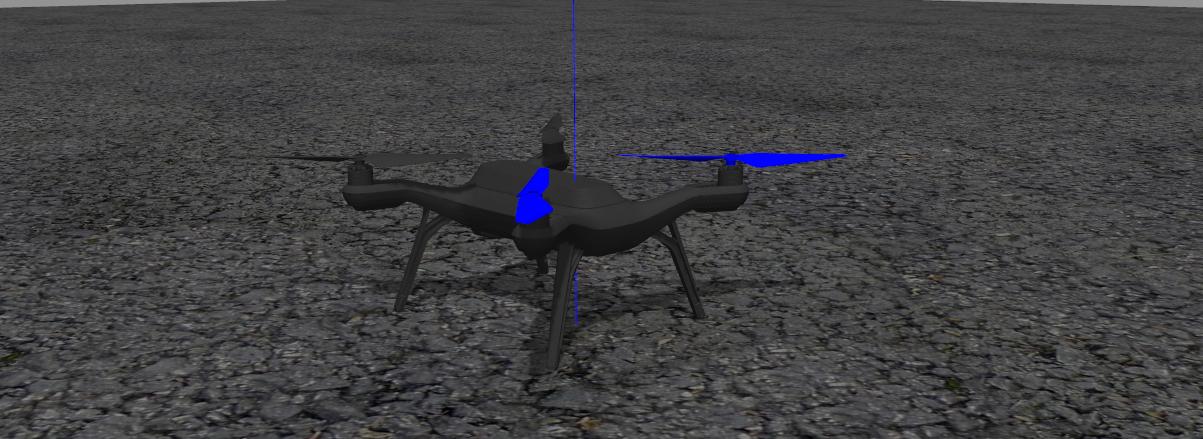
-
Standard Plane (
make posix gazebo_plane)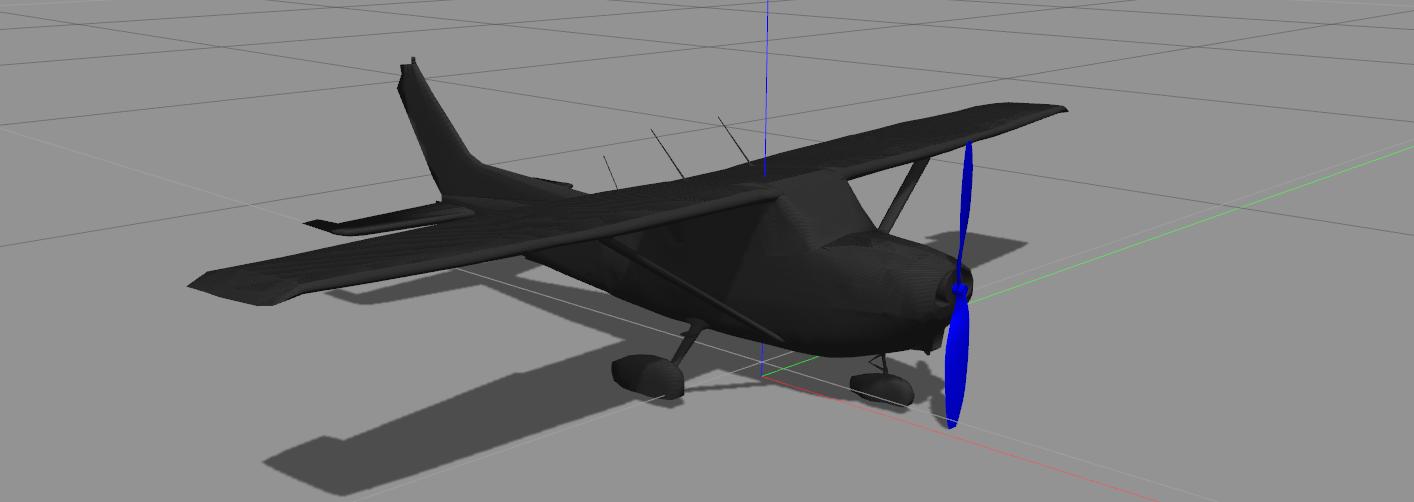
-
Standard VTOL(
make posix_sitl_default gazebo_standard_vtol)
-
Tailsitter VTOL (
make posix_sitl_default gazebo_tailsitter)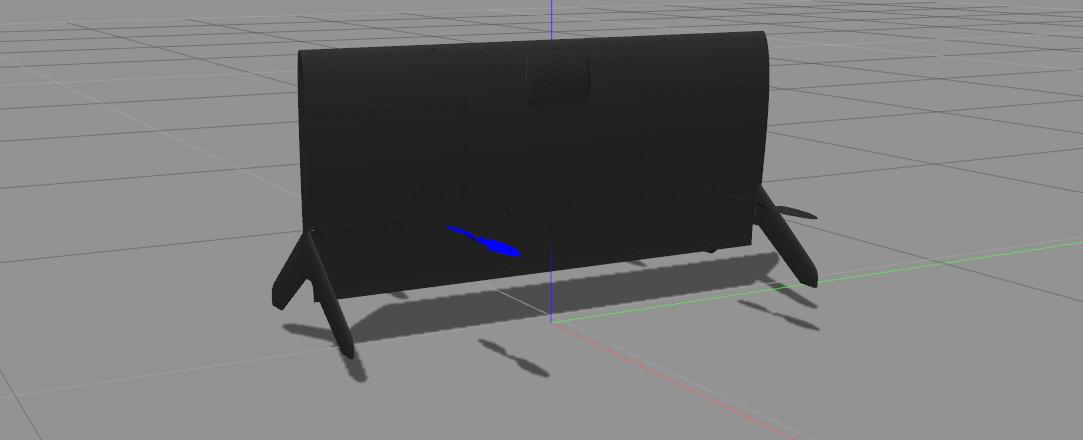
These are just a few of the targets there. They could be listed with make posix list_vmd_make_targets.
As explained on the documentation, you can type on the terminal commander takeoff, and the drone started flying
Everything is set now to command the drone. Let’s create a ROS node and start sending MAVLINK commands.
Happy droning!